How to buy Coca-Cola stocks in 2025

The Coca-Cola Company (KO) is one of accomplished investor Warren Buffett’s favourite stocks. He bought more than $1 billion in Coca-Cola shares — or 6.2% of the company — in 1988, which made it one of the largest holdings in his Berkshire Hathaway portfolio at the time. As of March 2021, Buffett’s holding company still had a stake in the company: 9.2% of the company, worth $22 billion.
You would therefore be in good company if you also chose to add this company to your portfolio, so let’s look at why you might want to, from a (mainly) fundamental analysis perspective. In short, let’s look at this Buffett stock using Buffett’s investment methodology.
How to Buy KOF Stocks in 5 Easy Steps
-
1Visit eToro through the link below and sign up by entering your details in the required fields.
-
2Provide all your personal data and fill out a basic questionnaire for informational purposes.
-
3Click 'Deposit', choose your favourite payment method and follow the instructions to fund your account.
-
4Search for your favourite stock and see the main stats. Once you're ready to invest, click on 'Trade'.
-
5Enter the amount you want to invest and configure your trade to buy the stock.
Top 3 Brokers to Invest in Coca-Cola
1. eToro
There are several reasons why eToro has won a spot on our list and has been heralded as having a large market share of traders. Thanks to its consistency over the years, eToro has gained the trust and loyalty of over 17 million users. You can read our full eToro review here.

Security and Privacy
Security and privacy are arguably the most important factors that determine your choice of a brokerage platform. eToro takes the privacy and security of its users very seriously. The platform adopts a thorough security procedure with fewer odds of loss or leakage of information. eToro is regulated by the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). The platform also adopts the two-factor authentication (2FA) method and uses SSL encryption to prevent security breaches.
Fees & Features
eToro operates a no-commission policy for deposits. However, to promote active trades on the platform, users are charged a monthly fee of £10 for the inactivity fee.
eToro offers a wide scope of offering cuts across several markets, including forex, stocks, and cryptocurrency, aiding an all-in-one trading experience.
Being a beginner-friendly platform, it offers the copy trading feature to help beginner traders leverage the advanced trading strategies used by expert traders. The platform itself also offers winning strategies to guide trade.
| Fee Type | Cost |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | £5 |
| Inactivity Fee | £10 (monthly) |
Pros
- Copy trading feature
- Ease of use for both new and experienced traders
- Operation across different financial markets
- No commission fee policy
Cons
- Customer service offerings are limited.
2. Capital.com
Capital.com is a reputable brokerage that supports trading on several financial markets. The provisions of its trading terms and the quality of innovation and efficiency of operation offered through the platform's features have granted it a market share of over 5 million users. Other benefits of the platform are no commission, low overnight fees, and tight spreads. You can read our full Capital.com review here.
Security and Privacy
Accredited by financial regulatory bodies including the FCA, CySEC, ASIC, and the FSA, Capital.com adheres to industry security guidelines in protecting its users. In addition, the platform complies with PCI Data Security Standards to safeguard customers’ information.
Fees & Features
Capital.com is popular for its offer of free brokerage services. With no hidden charges, inactivity charges, or withdrawal charges, Capital.com operates a transparent fee procedure. The bulk of the fees charged by Capital.com are Spread charges.
Capital.com’s mobile trading app has an AI-powered tool that provides clients with personalized transformation through its detection algorithm. In addition, the platform has an efficient and responsive customer support team serving multilingual customers via email, phone calls, and live chat channels round the clock.
| Fee Type | Cost |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | £0 |
| Inactivity Fee | £0 |
Pros
- Responsive customer support team
- Ease of use with the MetaTrader integration
- Commission-free trading policy
Cons
- CFDs restrictions.
3. Skilling
For a broker that originated in 2016, Skilling’s journey to the top has been impressive. The platform offers services across multiple asset trades, serves advanced trading strategies to experienced traders, and offers commission-free services. You can read our full Skilling review here.
Security and Privacy
Skilling is regulated and accountable to highly reputable financial regulatory bodies like the FSA and CySEC. In addition, the platform maintains a different bank account for monies paid by traders to enhance the security of funds.
Fees & Features
Skilling, like eToro and Capital.com, offers commission-free services. The fees are charged as Spreads and vary based on share type. Another upside to trading on Skilling is flexibility and choice. The platform offers two varieties of accounts for trading CFDs on forex and metals. The first is the Standard Skilling account with bigger spreads and no commissions. In contrast, the Premium account offers reduced spreads and charges commissions on spot metal and forex CFD trades. In addition, Skilling offers features such as a demo account, mobile apps, and a trade assistant.
| Fee Type | Cost |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | No fixed cost |
| Inactivity Fee | £0 |
Pros
- No-commission fee policy
- Responsive support team
Cons
- Technical for novice traders
- Service unavailable in countries such as U.S and Canada.
Everything You Need To Know About Coca-Cola
What do you need to know about The Coca-Cola Company? Here consider the company history, its strategy, how it makes money, and what its recent performance looks like.
Coca-Cola History
Named after its two principal ingredients — coca leaves and cola nuts — the original Coca-Cola drink was concocted by American pharmacist John Stith Pemberton in 1886. Rights to the drink's name and formula were bought from Pemberton's heirs by American businessman Asa Griggs Candler in 1889. The company was formally founded by Candler in 1895 and was subsequently sold to the Trust Company of Georgia in 1919. It became publicly listed the same year on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
While Coca-Cola commanded a massive 60% market share in 1948, this had fallen to less than 22% by 1984 due to competitors such as Persi.
The company has taken stakes in other companies over the years, including Minute Maid (1960), Monster Beverage (2014), and Costa Coffee (2018). Somewhat surprisingly, it owned Columbia Pictures from 1982 to 1989.
What is Coca-Cola’s Strategy?
According to its website, The Coca-Cola Company has several active initiatives:
- Water leadership because the company considers water quality and water efficiency to be important parts of its production.
- Reducing added sugar to address the global obesity epidemic and adapt to customers’ changing tastes.
- World without waste, which means reducing waste via goals such as curbing the use of virgin plastic from non-renewable sources.
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion to emulate the diversity of its consumer market, for example by having women represent 50% of its leadership.
How Does Coca-Cola Make Money?
Coca-Cola’s revenues come from the sale of various beverages: sparkling soft drinks, water, sports drinks, juice, dairy, tea, coffee, and energy drinks. Most of its products are sold by the Concentrate Business as concentrates and syrups to bottling facilities around the world, but some are sold by the Finished Product Business that owns some bottling operations. The company has four geographic business segments — North America, Latin America, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific — and two non-geographic segments: the Bottling Investment Group (BIG) and Global Ventures (GV).
How Has Coca-Cola Performed in Recent Years?
When Buffett went on a buying spree after the 1987 stock market crash, he picked up Coca-Cola shares in 1988/9 at less than one-tenth of the price they now stand at, as you can see in this price chart:
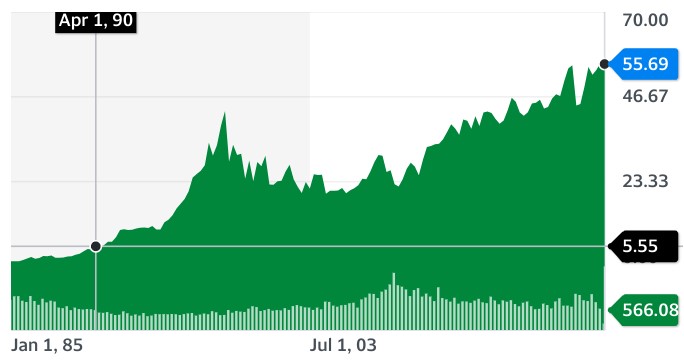
Although this price appreciation alone is no bad thing, it may not be where all the money was made from this stockholding. For many years, this stock has paid dividends at a yield of about 3% per year, which adds up to a lot of extra cash when reinvested and compounded over 30+ years.
Where Can You Buy Coca-Cola Stock?
If you want to be like Buffett and buy Coca-Cola stock for your own portfolio, you will find its shares listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) with the ticker symbol KO. You won’t interact with the stock exchange directly, so you’ll need a stockbroker that lets you trade American stocks.
Alternatively, many brokers in the UK and around the world will let you bet on a rising (or falling) Coca-Cola stock price via leveraged spread bets or contracts-for-difference (CFDs). Contrary to popular belief, you still benefit from the dividends when you trade via these financial instruments.
Coca-Cola Fundamental Analysis
Value investors favour fundamental analysis (checking a company’s financial health) over the technical analysis (chart reading) that is preferred by traders.
Coca-Cola’s Revenue
Revenue is shown on the “top line” of a company’s income statement. It shows the amount of money the business brings in from the sales of its products or services before any costs have been deducted to arrive at the company’s net earnings (or profits). The following figures show how The Coca-Cola Company’s revenues have been fairly consistent and predictable over the past few years.
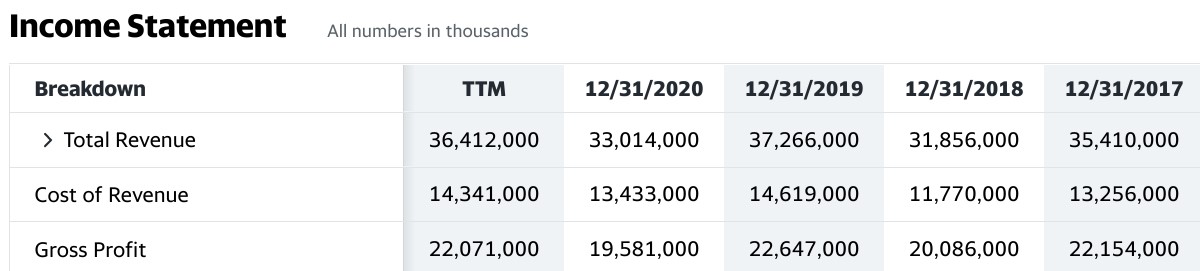
The Coca-Cola Company income statement showing revenue (source: Yahoo! Finance)
Coca-Cola’s Earnings-per-Share
Deducting a company’s costs from its revenues leads to the “earnings” figure that is also referred to as the “bottom line” of the income statement. Essentially, it’s the company’s profit that could be distributed to shareholders.
As a part-owner of the company, you’ll be interested in your proportion of the profit, which depends on the number of shares you hold. Simply put, you’ll be interested in the company’s earnings-per-share (EPS). Popular financial websites will tell you that Coca-Cola’s EPS figure to 31 December 2020 was USD $1.80.
Coca-Cola’s P/E Ratio
The next question is the price you have to pay to buy Coca-Cola shares to benefit from those earnings. At $55-per-share, and with earnings of $1.80-per-share, the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio would be about 30. In simple terms, this means it would take 30 years for the company to earn enough money to pay back the cost of your share purchase. Lower P/E ratios are usually — but not always — regarded as more attractive than higher ones, so this is a measure you can compare with other companies you might invest in.
Coca-Cola’s Dividend Yield
A company doesn’t have to pay out its earnings to shareholders, and many younger companies choose to plough profits back into the business, which should make the company more successful and more valuable. The Coca-Cola Company is one of several companies that does distribute a proportion of its profits to shareholders in the form of dividends, and it has done so for many decades.
For comparison purposes, a stock’s dividend relative to its current share price (the “dividend yield”) is more informative than the monetary amount of the dividends paid. This company’s forward dividend yield in September 2021 was stated on financial websites as 3.02%, which would make it more attractive than a bank deposit account paying 1% interest. However, with stocks, there is the additional negative risk that your capital could fall if the share price goes down (but also the positive risk that your capital could increase).
Coca-Cola’s Cash Flow
Another fundamental metric that value investors look at is a company’s cash flow, particularly the “free cash flow” reflecting money that can be used to fund the company’s expansion, to pay down some of its debt, or to pay out dividends, all of which may be good for you as an investor. Coca-Cola’s free cash flow increased steadily between 2017 and 2020, which is a good thing.
Why Buy Coca-Cola Stocks?
The fact that this is one of Warren Buffett’s favourite stocks will be a good enough reason for many investors to invest. However, you should do your own research and due diligence.
This company’s share price has been in an up-trend for more than two decades, and we all know that the trend is your friend when trading stocks. Its latest dividend yield (at September 2021) is 3%, which is a bank deposit-beating rate regardless of whether the share price continues to appreciate.
Expert Tip on Buying Coca-Cola Stock
“ Coca-Cola is the kind of stalwart stock that you’ll buy to hold for a long time and bank the dividends along the way. It’s not the kind of industry-disrupting momentum tech stock that will make you (or lose you) a lot of money by doubling or halving in price in a single day. So, it’s a stock for long-term investors rather than short-term speculators. ”
5 Things to Consider Before You Buy Coca-Cola Stock
There are at least five things you need to know before you buy Coca-Cola shares or any other stock.
1. Understand the Company
Famous value investors such as Warren Buffett, Benjamin Graham (one of Buffett’s early influencers), and Peter Lynch have espoused the benefits of really getting to know a company before you invest in its stock. Although it shouldn’t be your sole reason for investing, it does no harm for you to be a customer of the company, and in this context, you may be interested to know that Buffett reportedly drinks five cans of Coke per day.
2. Understand the Basics of Investing
Understanding the company behind the stock you want to invest in is one thing, but you also need to understand investing in general. Read as many investment books as you can lay your hands on to understand how to value companies, how to manage your money and risk, and (if interested) how to interpret chart price patterns. Many brokers (see next) let you practice with virtual money in a demo account, to learn the ropes before investing for real. This “paper trading” can help familiarise you with the mechanics of trading and investing but will not expose you to the “fear and greed” emotions that will (but shouldn’t) influence your buying and selling decisions in the real world.
3. Carefully Choose Your Broker
When investing in a company like Coca-Cola for the long run, you need a conventional stockbroker that simply lets you buy shares. You don’t need a broker that lets you place leveraged bets on rising and falling share prices or foreign exchange currency pairs via spread bets or contracts-for-difference (CFDs). You will certainly want to use a properly regulated broker that provides state-backed protection for a proportion of your investment funds, to cover you in the unlikely event that the broker goes bust. You might also want to choose a broker that offers a certain kind of account, such as a tax-efficient Stocks & Shares ISA or Self-Invested Personal Pension (SIPP) account in the UK.
4. Decide How Much You Want to Invest
Financial traders are often advised to commit no more than 1% to 2% of available funds to any single trade. Investors are typically advised to diversify across several stocks so that no single company failure can bring down your portfolio. Therefore, the question of how much you want to invest is more a matter of what proportion of funds you should allocate to any individual stock.
Even though Warren Buffett is a big fan of The Coca-Cola Company, it accounts for less than 8% of his Berkshire Hathaway portfolio at the time of writing, so even a (very unlikely) complete company failure would leave the portfolio 92% intact. This said, Apple accounts for more than 40% of the Berkshire Hathaway holdings, which is not a proportion you should aim for as an amateur investor. Ten different stocks from different sectors, each accounting for 10% of your invested funds, should be the minimum diversification to aim for.
However you allocate your investible funds, you should never invest more money than you can genuinely afford to lose. Never borrow to invest unless you really know what you’re doing, and don’t make long-term investments with money you might need in the near future (e.g., to pay your rent).
5. Decide on a Goal for Your Investment
Before investing in any stock, you should ask yourself about the purpose of your investment. For example, is it to provide you with a short-term speculative gain from price appreciation, or is it to provide you with many years of income from dividend distributions? How long do you intend to hold the stock in your portfolio?
Holding for a long time allows you to benefit from compounding.
You may remember from math class that compound interest is interest that you receive on the interest you have already received from an investment such as money in a bank deposit account. It all adds up to provide exponential returns, which means — according to the “rule of 72” — that your money will double in only 10 years if invested with a compounded interest rate of 7.2%. Stocks don’t pay interest, but you’ll achieve the same effect by investing in a stock with a 7.2% dividend yield as long as you reinvest the dividends rather than spending them.
It’s no secret that Warren Buffett’s favourite holding period is “forever” so that he can benefit from the compounded returns that can be achieved by reinvesting dividends. If Warren Buffett’s word isn’t good enough, consider that Albert Einstein is on record as describing compounding as the eighth wonder of the world!
The Bottom Line on Buying Coca-Cola Stocks
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this guide to buying Coca-Cola stocks, including:
- The company’s history, revenue streams, and recent performance.
- How to perform a fundamental analysis of the company’s financial health.
- Why you should consider buying the stock, and what other considerations you should take into account.
The bottom line is that you’d be in good company if you invest in The Coca Cola Company because it’s one of famous investor Warren Buffett’s favourite long-term stock holdings.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Although any stock with a continually shifting share price can be traded for speculative profit, The Coca-Cola Company may be better as a stock to buy and hold for a long time while collecting (and reinvesting) its regular dividend distributions. This is what Warren Buffett does.
-
It’s a value stock in the sense that Buffett bought it when it was undervalued; i.e., when the true intrinsic value of the company was not reflected in its share price. As a dividend-paying stock with a long history, it’s not like a “growth stock” such as Tesla that is setting out to disrupt established markets and whose share price reflects its future prospects.
-
The main rival to The Coca-Cola Company is PepsiCo, so this is a similar stock you could consider. Consumers tend to prefer the taste of Pepsi in blind taste tests yet Coke remains the market leader.
-
If you invest £1,000 in a stock that pays a 10% dividend (lucky you!), after one year you’ll have an extra £100 to buy more of the same stock. After another year, this combined £1,100 stockholding would pay you an increased £110 at the same dividend yield. Thus, the value of your holding snowballs in value if you keep reinvesting the dividends, because — in banking terms — it’s like earning interest on your interest.
-
This is entirely up to you, but bear in mind that you only pay capital gains tax when you sell shares, so you may want to time your share sales to fall within any annual tax-free allowances. Warren Buffett’s favourite holding period is “forever”.
-
American businessman, investor, and philanthropist Warren Buffett is one of the world’s most successful investors. Known as the Sage of Omaha after the Nebraska town where he was born and still lives, he is an adherent of the “value investing” approach pioneered by Benjamin Graham. Buffett is chairman and the largest shareholder of the Berkshire Hathaway holding company. Like his friend Bill Gates, he has pledged to give away much of his fortune to philanthropic causes.






