How to buy Caixa stocks in 2026

Formerly Criteria CaixaCorp, CaixaBank, S.A. is a Spanish multinational financial services company. Together with its subsidiaries, it provides banking and financial services — including insurance, asset management, and card services — in Spain and other parts of the world. The bank is based in Valencia but with operative offices in Madrid and Barcelona. Following its merger with Bankia in March 2021, CaixaBank became Spain’s largest lender by market value.
The bank’s stock is listed on the Bolsa de Madrid and is part of the IBEX 35 Index. This guide tells you how you can buy CaixaBank stock with confidence, and why you might want to, taking certain fundamental factors into account.
How to Buy CAIXY Stocks in 5 Easy Steps
-
1Visit eToro through the link below and sign up by entering your details in the required fields.
-
2Provide all your personal data and fill out a basic questionnaire for informational purposes.
-
3Click 'Deposit', choose your favourite payment method and follow the instructions to fund your account.
-
4Search for your favourite stock and see the main stats. Once you're ready to invest, click on 'Trade'.
-
5Enter the amount you want to invest and configure your trade to buy the stock.
Top 3 Brokers to Invest in Caixa
1. eToro
There are several reasons why eToro has won a spot on our list and has been heralded as having a large market share of traders. Thanks to its consistency over the years, eToro has gained the trust and loyalty of over 17 million users. You can read our full eToro review here.
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy are arguably the most important factors that determine your choice of a brokerage platform. eToro takes the privacy and security of its users very seriously. The platform adopts a thorough security procedure with fewer odds of loss or leakage of information. eToro is regulated by the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). The platform also adopts the two-factor authentication (2FA) method and uses SSL encryption to prevent security breaches.
Fees & Features
eToro operates a no-commission policy for deposits. However, to promote active trades on the platform, users are charged a monthly fee of £10 for the inactivity fee.
eToro offers a wide scope of offering cuts across several markets, including forex, stocks, and cryptocurrency, aiding an all-in-one trading experience.
Being a beginner-friendly platform, it offers the copy trading feature to help beginner traders leverage the advanced trading strategies used by expert traders. The platform itself also offers winning strategies to guide trade.
| Fee Type | Cost |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | £5 |
| Inactivity Fee | £10 (monthly) |
Pros
- Copy trading feature
- Ease of use for both new and experienced traders
- Operation across different financial markets
- No commission fee policy
Cons
- Customer service offerings are limited.
2. Capital.com
Capital.com is a reputable brokerage that supports trading on several financial markets. The provisions of its trading terms and the quality of innovation and efficiency of operation offered through the platform's features have granted it a market share of over 5 million users. Other benefits of the platform are no commission, low overnight fees, and tight spreads. You can read our full Capital.com review here.

Security and Privacy
Accredited by financial regulatory bodies including the FCA, CySEC, ASIC, and the FSA, Capital.com adheres to industry security guidelines in protecting its users. In addition, the platform complies with PCI Data Security Standards to safeguard customers’ information.
Fees & Features
Capital.com is popular for its offer of free brokerage services. With no hidden charges, inactivity charges, or withdrawal charges, Capital.com operates a transparent fee procedure. The bulk of the fees charged by Capital.com are Spread charges.
Capital.com’s mobile trading app has an AI-powered tool that provides clients with personalized transformation through its detection algorithm. In addition, the platform has an efficient and responsive customer support team serving multilingual customers via email, phone calls, and live chat channels round the clock.
| Fee Type | Cost |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | £0 |
| Inactivity Fee | £0 |
Pros
- Responsive customer support team
- Ease of use with the MetaTrader integration
- Commission-free trading policy
Cons
- CFDs restrictions.
3. Skilling
For a broker that originated in 2016, Skilling’s journey to the top has been impressive. The platform offers services across multiple asset trades, serves advanced trading strategies to experienced traders, and offers commission-free services. You can read our full Skilling review here.
Security and Privacy
Skilling is regulated and accountable to highly reputable financial regulatory bodies like the FSA and CySEC. In addition, the platform maintains a different bank account for monies paid by traders to enhance the security of funds.
Fees & Features
Skilling, like eToro and Capital.com, offers commission-free services. The fees are charged as Spreads and vary based on share type. Another upside to trading on Skilling is flexibility and choice. The platform offers two varieties of accounts for trading CFDs on forex and metals. The first is the Standard Skilling account with bigger spreads and no commissions. In contrast, the Premium account offers reduced spreads and charges commissions on spot metal and forex CFD trades. In addition, Skilling offers features such as a demo account, mobile apps, and a trade assistant.
| Fee Type | Cost |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | No fixed cost |
| Inactivity Fee | £0 |
Pros
- No-commission fee policy
- Responsive support team
Cons
- Technical for novice traders
- Service unavailable in countries such as U.S and Canada.
Everything You Need To Know About Caixa
Now, let’s get to know CaixaBank in more detail by exploring its history, business strategy, and several other insights regarding this company.
Caixa History
Founded in Barcelona in 2007 as Criteria CaixaCorp, the firm started as a publicly-traded company. Criteria CaixaCorp’s initial public offering was the largest-ever in Spain as of 2007. Subsequently, the stock was promoted to the IBEX 35 index in January 2008.
In 2011, Criteria CaixaCorp was renamed CaixaBank when it merged with La Caixa's banking and insurance company. At that time, most of Criteria’s industrial stakes were divested, but CaixaBank retained stakes in Repsol YPF and Telefónica as well as all holdings in other financial services companies.
CaixaBank absorbed Banca Cívica in the third quarter of 2012. In November of the same year, it decided to buy Banco de Valencia, which was at that time nationalised. Following the political crisis in Catalonia in 2017, the bank moved its headquarters to Valencia. In March 2021, CaixaBank merged with Bankia, making CaixaBank the largest bank in Spain.
What Is Caixa’s Strategy?
CaixaBank offers retail, corporate, and institutional banking, as well as insurance, asset management, card services, cash management, and market services. The company also holds a portfolio of real estate assets and has stakes in the oil and gas firm Repsol and the telecommunications company Telefónica.
The CaixaBank Group uses a “people first” strategy, which has helped it to remain the leading group in retail banking in Spain while continuing to grow its services in Portugal, among other countries. Its strategy focuses on improving customer experience by transforming the branch network, expanding remote and digital service models, enriching the products and services ecosystem, and reviewing customer journeys via experience maps.
How Does Caixa Make Money?
The company makes money from its universal banking and insurance services, as well as from its stakes in the oil and gas firm Repsol, the telecommunications company Telefónica, and its holdings in several other financial institutions.
For its commercial banking services, it makes money from the interest it charges for lending out money to individuals, SMEs, and corporations. Its investment banking subsidiary makes money from the fees it charges for its investment banking and advisory services, as well as from its trading activities in the financial markets. The bank’s insurance section makes money from the premiums collected from insurance coverage and the fees associated with its asset management services.
How Has Caixa Performed in Recent Years?
The stock has been swinging up and down since it was publicly listed in 2007. Generally, it has been on a decline: as of October 2021, it’s trading around €2.68 compared to €5.44 in 2007. Its all-time of €5.66 was just a spike in January 2011. In fact, its first day’s close of €5.25 has been the highest price it has closed since the day it was listed.
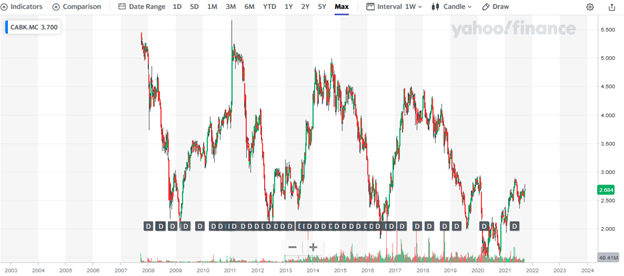
Source: Yahoo! Finance
Where Can You Buy Caixa Stock?
Trading a stock CFD or simply spread betting is different from buying the actual stock from a stockbroker. With CFD trading, you are only speculating on the price movements of the stock without owning it. To own CaixaBank stock, you have to buy it through an international stockbroker with access to the Bolsa de Madrid. However, some CFD providers can also allow you to buy real stocks.
While most international stockbrokers offer only the standard share dealing accounts, UK-based ones also offer the tax-efficient shares ISA and SIPP accounts. It’s also possible to buy CaixaBank DR from the dealing arm of any major international bank in your country.
Caixa Fundamental Analysis
Unlike technical analysis in which traders use a stock’s historical price action to forecast its future price movements, fundamental analysis is used by investors to evaluate a stock by studying the company’s business to know its financial health and intrinsic value.
There are many factors investors consider when evaluating a stock using fundamental analysis, including non-measurable ones like company management and track record. But in this guide, we will focus on the measurable financial metrics, such as the company’s revenue, earnings-per-share, P/E ratio, dividend yield, and cash flow.
Caixa’s Revenue
Also referred to as the top line, revenue is the amount of money a company makes from the sale of its products or services. It is presented at the top of the company’s income statement in its quarterly or yearly report or on the website of your broker.
Year-on-year or quarter-for-quarter revenue growth shows that the company is able to make more sales, which, all things being equal, would translate to more earnings. In the 2020 fiscal year CaixaBank reported revenue of €9.01 billion. This implies a 1.1% decline from the 2019 revenue. The 2020 fiscal year was a tough one for most businesses due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
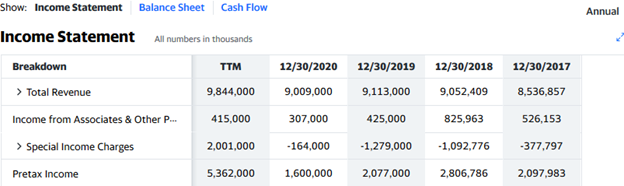
Source: Yahoo! Finance
Caixa’s Earnings-per-Share
A company’s net earnings, also referred to as the bottom line, are the profit left after subtracting all costs of doing business from the revenue. But what is more important to you is the earnings per share (EPS) because you only own some shares in the company, not the entire company.
To calculate the EPS, you divide the company’s total earnings (less the dividends paid to preferred stockholders) by the number of outstanding shares of its common stock. However, you don’t need to calculate the EPS by yourself since you can get that from your stockbrokers’ website or any of the major financial websites. CaixaBank’s annual EPS for the 2020 fiscal year was €0.21.
Caixa’s P/E Ratio
A company’s P/E ratio (price-to-earnings ratio) compares its share price to its earnings-per-share. You get the value by dividing the current share price of the stock by the annual EPS. Considering CaixaBank’s share price of €2.635 at the time of writing and its annual EPS of €0.21 for the 2020 fiscal year, the company’s P/E ratio would be about 12.55 (2.635/0.21).
So, investors are willing to pay €12.55 for every euro the company earns in profits. To put it differently, they are willing to wait for more than 12 years to recoup their investment from earnings alone, assuming the earnings remain the same every year.
Generally, a high P/E ratio often indicates that the stock is overvalued, but there is actually no cutoff value for the P/E ratio. Investors often compare with those of similar stocks to get an idea of what is high or not. Also, the P/E ratio doesn’t factor in earnings growth, which is why you should check the PEG ratio since it gives the growth-adjusted P/E value.
Caixa’s Dividend Yield
Dividends are payments a company makes to its shareholders as their share of the company’s earnings. These payments can come quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. CaixaBank has a history of paying dividends, and it paid a dividend of €0.0268 for the 2020 fiscal year. Whenever dividends are declared, the share price rises until the ex-dividend date and falls afterwards.
Investors use the dividend yield to know how the total annual dividend compares to the share price. For example, given CaixaBank’s annual dividend of €0.0268 per share for the 2020 fiscal year and a share price of €2.635, the dividend yield is 1.02% (0.0268/2.635). You can see it along with other financial ratios on your stockbroker’s website or any of the major financial websites, so you don’t have to calculate it yourself.
Caixa’s Cash Flow
Cash flow refers to how a company generates and spends cash and cash equivalents. This is recorded in the cash flow statement, which you can see beside the other financial statements in the financial section of the company’s information on a broker’s website or any of the major financial websites, as in the picture below:
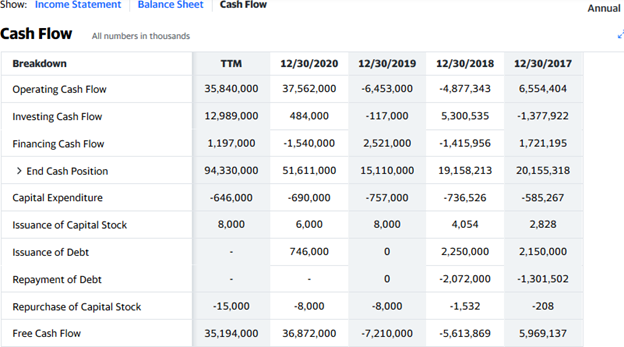
Source: Yahoo! Finance
The most important figure in the cash flow statement is the free cash flow because it shows how much cash the company has left after paying for major expenses. From the image above, CaixaBank had about €36.9 billion in free cash flow by the end of the 2020 fiscal year. That is the cash the company can use to fund expansion, pay dividends, or pay down debts.
Why Buy Caixa Stocks?
Like most bank stocks, CaixaBank stock is cyclical, rising and falling in line with the state of the economy. Even when compared with its peers, the stock has been performing poorly since it became public (never closed above its first day’s open price). Despite the poor performance, the firm has a growth mindset and has been making key acquisitions. It also invests in non-financial assets.
These are some of the reasons you might want to buy CaixaBank stock:
- The company is innovative and has an expansionary mindset;
- It has a history of paying regular dividends;
- Following its acquisition of Bankia, the bank is the largest lender in Spain.
Expert Tip on Buying Caixa Stock
“ The stock’s price movement is cyclical, so it’s better to buy at the dip and ride up the next upswing. In other words, its share price tends to go up and down with the business cycle. Moreover, buying the stock cheaper at the low point of the cycle will also improve your dividend yield. So, if a new swing is already underway, you may want to wait for the next dip. ”- willfenton
5 Things to Consider Before You Buy Caixa Stock
Be sure to consider these five things before you buy any stock:
1. Understand the Company
It may be reasonable to invest in a company you are familiar with and even use their products or services. But, this is not enough reason to invest in a stock if you don’t also consider the fundamental factors. It is necessary to study the company to understand its business model and how it makes money. While you may be banking with CaixaBank and even like its services, the bank may be running at a loss from year to year, which makes it a bad stock to invest in.
2. Understand the Basics of Investing
Be sure to learn the basics of investing before putting money in the market. It helps to understand how the market works and what you can do to protect your capital so you don’t just throw your money away. You need to learn how to execute orders and when to use a limit or a market order. Another aspect is how to manage risks: study money management and risk management techniques, as well as diversification methods.
3. Carefully Choose Your Broker
While there are many stockbrokers to choose from, ensure that the stockbroker you choose is regulated in your country of residence. Among others, it allows you to benefit from any fund insurance scheme available in your country, such as the financial services compensation scheme (FSCS) in the UK. Other factors you should consider before choosing a broker include customer support services, payment methods, trading fees, trading platform and tools, and supported order types.
4. Decide How Much You Want to Invest
It’s important to determine how much you want to invest and the percentage to allocate to each stock. You should also plan how you want to put the money in the market: it is possible to invest the lump sum at once, but it may be better to scale in at intervals so as to reduce the impact of volatility.
One more thing, it is very important you invest with an amount you can afford to lose, and if you are a beginner, avoid using leverage, no matter how profitable the stock appears to be — leverage can magnify both your gains and losses.
5. Decide on a Goal for Your Investment
Finally, you have to define your investment goal. What is the reason for investing? It could be that you want to build a pension fund for retirement or raise money for your kids’ college. Whatever the reason, be sure to plan when you would cash in on your investment. Is it when the price reaches a particular level, when the fundamentals no longer stack up, or when your kids reach a certain age? Be sure to write your plan down and stick to it.
The Bottom Line on Buying Caixa Stocks
CaixaBank, S.A. is a Spanish multinational financial services company that offers banking, investment, and insurance services. You may want to invest in this leading Spanish bank to enjoy regular income from dividend payments, but you will need to go through an international stockbroker with access to the Bolsa de Madrid where the stock trades.
If you’re ready to invest in CaixaBank stock right now, sign up for a stockbroker’s share dealing account and look for the stock on its platform. Then, place a buy order, which can be a market or limit order.
If you’re not ready to invest right now, continue to read other guides on our website to get more information about investing. You may also “paper trade” with a stockbroker’s demo account to learn how to place orders.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Revenue is often referred to as the top line because it is placed at the very top of a company's income statement. It is the first figure displayed before the cost of sales is deducted to get the gross profit. When a company’s revenue increases, it is said to be generating top-line growth.
-
A company’s net income is sometimes referred to as the bottom line because it is the last figure displayed on the income statement — it is displayed at the bottom line of the income statement. The net income is reached after all expenses, taxes, and interests have been deducted from the revenue.
-
The price/earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratio compares a company’s P/E ratio to its expected earnings growth rate. It is calculated by dividing the P/E ratio by the growth rate of its earnings for a specified period. This metric helps investors factor in future earnings growth prospects when valuing a stock.
-
A market order, also known as “at best order” is an order to buy or sell a stock at the best available price in the market at that moment. While a market order ensures fast execution of the trade, it does not guarantee a specified price. So, it is best for those who want their trades executed immediately.
-
When dividends are declared, investors rush to buy the stock to qualify for the dividend. This creates a higher demand for the stock. By the ex-dividend date, the company draws the line on their book so that those buying the stocks afterwards cannot qualify for the dividend. This reduces interest in the stock, driving demand down.
-
It is necessary if you plan to benefit from short-term price swings. Fundamental analysis alone may not be enough, as it can only tell you if the stock is worth buying and holding in the long term. It typically does not tell you the right moment to buy the stock in case your time horizon is 6 months or shorter.






