How to buy Orange stocks in 2026

Formerly France Télécom S.A., Orange S.A. is a French multinational telecommunications corporation that serves over 266 million customers in France, other European countries, Middle East, and Africa. Headquartered in Paris, it is the third largest telecom operator in Europe after Vodafone and Telefónica. The company provides landline and mobile telecommunications, data transmission, and internet and Internet Protocol television (IPTV) services.
Orange stock trades on the Euronext Paris stock exchange and is a component of the CAC 40 Index. This guide tells you how you can buy Orange stock with confidence and the reasons to do so, taking various fundamental factors into account.
How to Buy ORAN Stocks in 5 Easy Steps
-
1Visit eToro through the link below and sign up by entering your details in the required fields.
-
2Provide all your personal data and fill out a basic questionnaire for informational purposes.
-
3Click 'Deposit', choose your favourite payment method and follow the instructions to fund your account.
-
4Search for your favourite stock and see the main stats. Once you're ready to invest, click on 'Trade'.
-
5Enter the amount you want to invest and configure your trade to buy the stock.
Best Reviewed Brokers to Buy Orange Stocks
1. eToro

eToro is one of the most prominent social investment networks, with a mission to improve investors' knowledge and activity regarding finance. Since its inception in 2007, eToro has become the premier investment platform for novice and experienced traders, with a user base of over 17 million. You can read our full eToro review here.
Security and Privacy
When choosing an investment platform, security is among the biggest factors to consider. Since eToro is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC), you can be assured that your funds and personal details are secure. Furthermore, eToro SSL encrypts all submissions to safeguard against hackers trying to intercept confidential information. Finally, the platform has two-factor authentication (2FA) to ensure the users’ accounts are safe.
Fees & Features
Both inexperienced and seasoned investors can take advantage of eToro's extensive library of cutting-edge trading methods. For instance, beginners in trading can take advantage of CopyTrading available on eToro as it allows them to mimic the actions of more experienced traders. Those with trading experience will be glad to find that eToro provides access to many markets, such as stocks, currencies, and cryptocurrency, all from one platform. Also, eToro is a commission-free service. However, the platform charges a monthly fee of £10 for inactivity to promote active trades on the platform.
| Fee Type | Fee Amount |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Withdrawal Fee | £5 |
| Inactivity Fee | £10 (monthly) |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
Pros
- Copy trading feature
- SSL encryption to protect users' information
- Trading is commission-free
Cons
- Limited customer service
2. Capital.com

Capital.com, which originated in 2016, is an excellent multi-asset broker. With over 5 million users, it has established itself as a low-cost platform with low overnight fees, tight spreads, and 0% commission. You can read our full Capital.com review here.
Security and Privacy
Capital.com is an FCA, CySEC, ASIC, and NBRB-licensed corporation dedicated to providing the most effective trading experience in the world. It shows that users' data is secured and hidden on Capital.com, since the site follows stringent criteria to achieve this goal. Capital.com takes client data security seriously, and one way it does this is by complying with the PCI Data Security Standards.
Fees & Features
Capital.com offers a wide variety of no-cost brokerage services. Its financial policies are transparent. Any fees you incur will be made clear before you pay them. Capital.com's principal costs come from spread charges, which are often low compared to competitors. The broker's mobile trading app features an AI-powered tool that gives clients personalized trading information by employing a detection algorithm. In addition, Capital.com's multilingual customers can get in touch with a representative via email, phone, or live chat.
| Fee Type | Fee Amount |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
| Commission Fee | 0% |
| Inactivity Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | £0 |
Pros
- Efficient email and chat support
- MetaTrader integration
- Commission-free trading
Cons
- Majorly restricted to CFDs
3. Skilling
Skilling is a multi-asset broker with significant growth. The broker offers excellent trading conditions regarding platform features and products available to experienced traders. Skilling now provides Forex, CFD, Stock, and cryptocurrency trading six years after its inception to individual investors. You can read our full Skilling review here.
Security and Privacy
When looking for a broker like Skilling, it is essential to check the broker's regulatory standing. Skilling is administered by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC). In addition, the money that traders deposit into their Skilling accounts is held in a completely independent financial institution. For maximum safety, Skilling only uses top-tier financial institutions for this purpose. Tier 1 capital is the industry benchmark for measuring a bank's soundness.
Fees & Features
Skilling does not charge commissions for trading equities, indices, or cryptocurrencies. The platform charges Spreads which vary based on the share, but are typically very reasonable. Skilling offers two distinct account options for FX and metals CFD trading. The Standard Skill account has significantly larger spreads but no commissions. The Premium account charges commissions on spot metal and FX CFD trades for decreased spreads. Additionally, Skilling provides a demo account, mobile applications, and a trade assistant.
| Fee Type | Fee Amount |
| Commission Fee | £0 |
| Withdrawal Fee | Varies |
| Inactivity Fee | £0 |
| Deposit Fee | £0 |
Pros
- Great platform choice
- Demo accounts
Cons
- High Spreads
- Service is unavailable in many countries, including the US and Canada.
Everything You Need To Know About Orange
At this point, let’s get to know Orange S.A. in more detail by exploring its history and business strategy, how it makes money, and how it has performed in recent years.
Orange History
Orange S.A. traces its history to 1991 when Hutchison Telecom, a UK subsidiary of the Hong Kong-based conglomerate Hutchison Whampoa, bought a controlling stake in Microtel Communications Ltd and renamed Microtel to Orange Personal Communications Services Ltd.
In October 1999, Hutchison Telecom sold Orange to the German conglomerate Mannesmann AG acquired for US$33bn. In February 2000, Vodafone acquired Mannesmann for US$183 billion. However, Vodafone had to divest Orange since the EU regulations wouldn't allow it to hold two mobile licenses.
So, in August 2000, France Télécom bought Orange plc from Vodafone for a total estimated cost of €39.7 billion and merged it with its other mobile services. It then renamed the new group Orange S.A. In March 2001, Orange S.A. was listed on the Euronext Paris stock exchange, with a secondary listing on the London Stock Exchange and New York Stock Exchange. In May 2001, Orange S.A. became a component of the CAC 40 Index, which represents the top 40 French companies by market capitalisation.
What Is Orange’s Strategy?
Orange S.A. provides fixed telephony and mobile telecommunications, data transmission, and other value-added services to individuals, businesses, and other telecommunications operators worldwide. It also sells mobile handsets, broadband equipment, and connected devices and accessories.
The company’s strategic plan includes evolving its network operator model to include 5G capabilities, accelerating in growth areas, prioritising data and AI (Artificial Intelligence) in its model, and co-creating with its employees a future-facing company.
It plans to tap into the growth potential in Africa and Middle East regions for both individual and business customers. Orange believes that its strength lies in reconciling business performance and a sustainable approach with our customers, employees, stakeholders, partners, and society in general.
How Does Orange Make Money?
Orange S.A. makes money from the sale of its services, which it offers under the following segments: IT services and software, telecoms services, digital content TV and video services, and Internet services. The company also makes money from the sale of network equipment, mobile phones, and other smart devices, which are intermediate goods that are automatically part of the added value.
In terms of geographical segments, the company categorises its services into five regions: North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and Africa & Middle East.
How Has Orange Performed in Recent Years?
Orange S.A. stock has been on a decline since 2001, despite making an effort to rally in 2003 and again in 2007-2008. From its all-time high of $209.94, the stock fell as low as $9 before rallying to the region of $17-$18. Since 2014, it has been trading sideways in the $14-$18 region before the coronavirus pandemic in 2020 forced the stock down to the $10-$12 range.
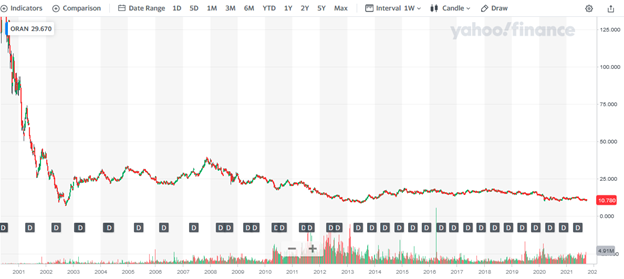
Source: Yahoo! Finance
Where Can You Buy Orange Stock?
Buying the actual stock from a stockbroker offers you part ownership in the company while trading the CFD or spread betting is simply speculating on the price movements of the stock without owning it. If you want to own Orange S.A. stock, you have to buy it through a stockbroker with access to the NYSE, Euronext Paris, or LSE where the stock trades, rather than through a CFD trading or spread betting platform, although some CFD providers also allow you to buy real stocks.
Most stockbrokers offer only the standard share dealing accounts, but UK-based ones also offer shares ISA and SIPP accounts, which are tax-efficient. You can also buy Orange S.A. DR from the dealing arm of any major international bank in your country.
Orange Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a method of evaluating a stock by studying the company’s business to know its financial health and intrinsic value. Some of the factors investors consider when evaluating a stock using fundamental analysis are non-measurable. However, in this guide, we will focus on measurable financial metrics, such as the company’s revenue, earnings-per-share, P/E ratio, dividend yield, and cash flow.
Orange’s Revenue
A company’s revenue is the amount of money it makes from the sale of its products or services. It is presented at the top of the company’s income statement in its quarterly or yearly report or on the website of your broker, which is why it is called the top line.
When there is year-on-year or quarter-for-quarter revenue growth, the stock is likely to perform better than when there is a revenue decline. In the 2020 fiscal year, Orange S.A. reported revenue of €42.27 billion, which represents a 0.8% increase in revenue compared to the 2019 value.
Orange’s Earnings-per-Share
A company’s net earnings represent the net profit after subtracting all costs of doing business, taxes, and other charges. Since you only own some shares in the company, not the entire company, you should be more concerned with the earnings per share (EPS), which is calculated by dividing the company’s total earnings (less the dividends paid to preferred stockholders) by the number of outstanding shares of its common stock.
However, you don’t need to calculate the EPS by yourself since you can get that from your stockbrokers’ website or any of the major financial websites. The annual EPS of Orange S.A. for the 2020 fiscal year was €1.72.
Orange’s P/E Ratio
A company’s P/E ratio (price-to-earnings ratio) is a metric that compares its share price to its earnings-per-share. It is calculated by dividing the current share price of the stock by the annual EPS, but you can see it on your broker’s website or any major financial website. Orange S.A.’s P/E ratio (TTM) is 30.228, which means that investors are willing to pay $30.28 for every $1.00 the company earns per share.
While a high P/E ratio generally indicates that the stock is overvalued, there is actually no cutoff value for the P/E ratio. So, investors try to compare with those of similar stocks to get an idea of what is high or not. But it is better to also check the PEG ratio since it factors in earnings growth rate.
Orange’s Dividend Yield
Companies pay dividends to their shareholders as a way to distribute the earnings for that accounting period to the owners of the company. They usually make these payments quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly. Orange S.A. paid a dividend of €0.90 for the 2020 fiscal year. The share price tends to rise whenever dividends are declared, but then, it starts to fall from the ex-dividend date.
The dividend yield shows how the total annual dividend compares to the share price, and investors use it to gauge the returns they get from investing in the stock. For example, Orange’s annual dividend for the 2020 fiscal year was €0.90 per share and the share price is €9.28 (Oct. 1, 2021), so the dividend yield is 9.70% (0.90/9.28). But, you don’t have to calculate it yourself, as you can see it along with other financial ratios on your stockbroker’s website or any of the major financial websites.
Orange’s Cash Flow
The cash flow statement is a financial statement that records how a company generates and spends cash and cash equivalents. You can see it beside the other financial statements in the financial section of the company’s information on a broker’s website or any of the major financial websites.
You should focus on the free cash flow because it shows how much cash the company has left after paying for major expenses. It is the cash the company can use to fund expansion, pay dividends, or pay down debt. From Orange S.A.’s cash flow statement below, you can see that the company had about €4.15 billion in free cash flow by the end of the 2020 fiscal year.
Why Buy Orange S.A. Stock?
As an innovative telecommunication stock that stands to benefit from the 5G trend, Orange S.A. has huge growth prospects, despite its poor performance over the years. The company is the third-largest mobile operator in Europe and also has a presence in many other regions worldwide. It plans to accelerate its growth areas and use innovative ideas like AI to improve its services.
Here are three reasons you might want to buy Orange S.A. stock:
- The company is an established telecom company with the capacity to innovate and expand;
- It stands to benefit from the 5G trend in the market;
- It has a history of paying dividends.
Expert Tip on Buying Orange Stock
“ Although the stock has been on a decline for a long time, it still has the potential to perform well. However, owing to the huge volatility in the stock, it is better to buy on a dip than to buy on a breakout. Also, it may be preferable to place a limit order to specify the price at which you want to buy. ”- willfenton
5 Things to Consider Before You Buy Orange Stock
These are the five things you need to consider before you buy Orange S.A. stock.
1. Understand the Company
Peter Lynch and Warren Buffett believe that it’s best to invest in a company you are familiar with. While this advice may be valid, it is not enough if you don’t consider key fundamental factors that can tell you about the financial status of the company. That you are using Orange S.A services doesn’t make it a great company: you must find out how it makes money if it has been making money, and how it is managed.
2. Understand the Basics of Investing
It’s important to learn the basics of investing before committing money to the market. Learn how to place orders in the market using your broker’s platform. You may want to practice paper trading to get familiar with the tools on your broker’s platform and understand how the market works. This can help you avoid some common mistakes like placing the wrong trade order. You should also try to become familiar with concepts like money management, risk management, and diversification techniques.
3. Carefully Choose Your Broker
Before you choose a broker to trade with, you need to consider certain factors, such as the broker's trading fees and commissions, customer support services, ease of deposit and withdrawal, trading channels and platform, supported order types, and regulation status.
The regulation status, especially in your country of residence, is very important as it makes your broker trustworthy. It also qualifies you to benefit from any compensation scheme in your country in case the broker goes bankrupt.
4. Decide How Much You Want to Invest
You should know how much you plan to invest and how to source the funds. It may be necessary to save your disposable income for a while to raise a reasonable amount. Whatever you do, make sure you don’t invest the money you need to take care of yourself and pay your bills.
When you have saved enough money to invest, plan how you put the money in the market. Investing all the money at one go may not be the best idea due to volatility. It may be preferable to gradually scale in and build your position of time.
5. Decide on a Goal for Your Investment
Do you have an investment goal? You must have it to be able to plan your activities in the market. Your goal may be to build a retirement fund or raise money for some future projects. But you need to see how it affects the time you recoup your investment. Do you sell your stocks when you reach a certain age or when the price reaches a certain level? You may have to consider the fundamentals to know when the company is in a weak situation. However, you may also decide to hold your positions indefinitely and sell when you need money.
The Bottom Line on Buying Orange Stocks
Orange S.A. is a French multinational company that offers fixed telephony and mobile telecommunication, data transmission, and internet services worldwide. You might want to buy this stock to benefit from the 5G trend in the market, and you can buy it from any broker with access to Euronext Paris or the NYSE.
Are you ready to invest in Orange S.A. stock right now? If yes, sign up for a stockbroker’s share dealing account, look for the stock on its platform, and place a buy order, which can be a market or limit order.
If you’re not ready to invest right now, keep reading other guides on our website to get more information about investing. It may be necessary to “paper trade” with a stockbroker’s demo account to learn how to place orders.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Also known as a market order, “at best” trade order is an order to buy or sell a security at the current best available price in the market. This type of order gets your trade executed immediately, but you may not get in at a good price if the volatility is high. That is, your entry price may be different from what you intended.
-
A limit order is a type of trade order that allows you to set the price at which you want your trade to be executed. With this type of order, your trade would only be executed at the pre-set price or a better price when the price reaches that pre-set level. For a buy order, the limit order is set below the current market price, while for a sell order, it is set above the current market order. Although a limit order allows you to enter at your preferred price or a better one, the trade may never get executed if the price doesn’t reach that pre-set level.
-
This is the actual or expected increase in profits over two comparable periods, which can be either year-on-year or quarter-on-quarter. For instance, if a company earned $2 billion in profit in 2019 and $2.1 billion in 2020, the earnings growth would be 5% YoY (year-on-year). Apart from the total earnings, you can also measure EPS growth.
-
Money management refers to how much of your trading capital you commit to each trade. Committing 50% of your trading capital to one trade is riskier than committing only 5%. If anything goes wrong, you would lose 50% of your capital in the former, and in the latter, you would only lose 5% of your capital and still have 95% to trade with. How much money you commit in each trade will determine your position size.
-
Yes, a stop-loss order helps to get you out of the market if the conditions are unfavourable for your position. It gets you out with a small loss and preserves your capital for new opportunities that will arise in the future. However, ensure you don’t set your stop-loss order close to your entry-level so that normal price gyrations don’t hit you out of your trade when the opportunity is still valid; that would lead to unnecessary losses.
-
Diversification helps you to spread your capital across non-correlating stocks and even across different asset classes. The idea is that if one investment is performing poorly, other assets that are doing well would compensate for the losses in the poorly performing asset.






